Plant Information
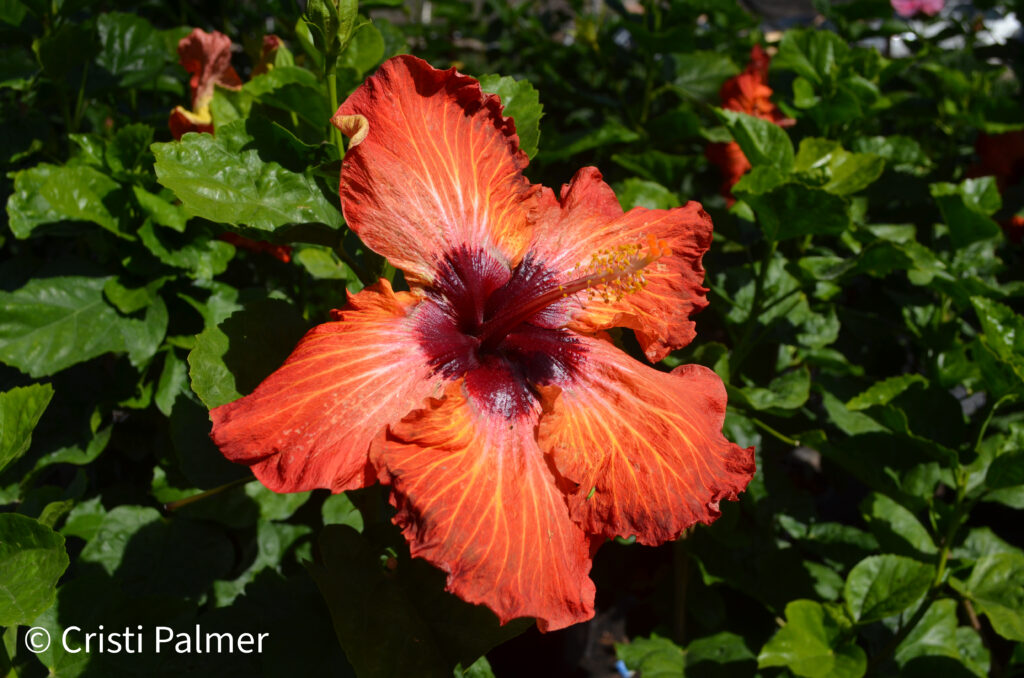

Hibiscus, which is commonly referred to as rose mallow, is a genus of flowering plants that belong to the Malvacea family. Hibiscus can be both perennial or annual herbaceous plants, woody shrubs and small trees. They are native to Asia and North America and there are over two hundred species and many more cultivars and hybrids available.
Hibiscus are typically grown for their large, beautiful flowers which area very attractive to butterflies and hummingbirds. Regardless of variety, hibiscus flowers are colorful and will add beauty to any landscape.
Planting and Maintenance
The type of care your hibiscus will need depends on whether the plant is hardy or tropical and this choice could be made by where you live. Although both types of hibiscus plants have similar flowers and enjoy full sun, hardy hibiscus plants are very different from the tropical varities that are grown indoors.
Tropical hibiscus varieties can be grown outdoors if you live in or south of zone nine. They tend to need moist but well-drained soil. Although warm, humid conditions are ideal for tropical hibiscus, you may want to plant in an area that provides afternoon shade. Tropical hibiscus can be found in single or double bloom varieties and have deep green, glossy leaves. Flowers come in a wide range of colors including peach, orange, pinks and yellow.
For those living in other, not so tropical climates, a perennial, hardy variety will be a better choice as it can withstand colder temperatures. Hardy hibiscus is a non-tropical plant that with protection, can tolerate weather as far north as USDA plant hardiness zone four. Hardy hibiscus can only be found with large, single blooms in colors such as red, white and pinks. Foliage have heart shaped leaves that are dull green in color. It is common for hardy hibiscus plants to die after a hard frost in the fall. When this occurs, cut them back to about 4 or 5 inches in height. Re-growth should start by late spring.
When plants are blooming they require large amounts of water. Your hibiscus will need daily watering in warm weather. Keep in mind that once the weather cools these plants will need much less water, and over-watering could actually cause the plant to die.
Economics
According to the USDA NASS Census of Horticulture, hibiscus sold for a wholesale value of $33.4 million in 2014 and $41.7 million in 2019.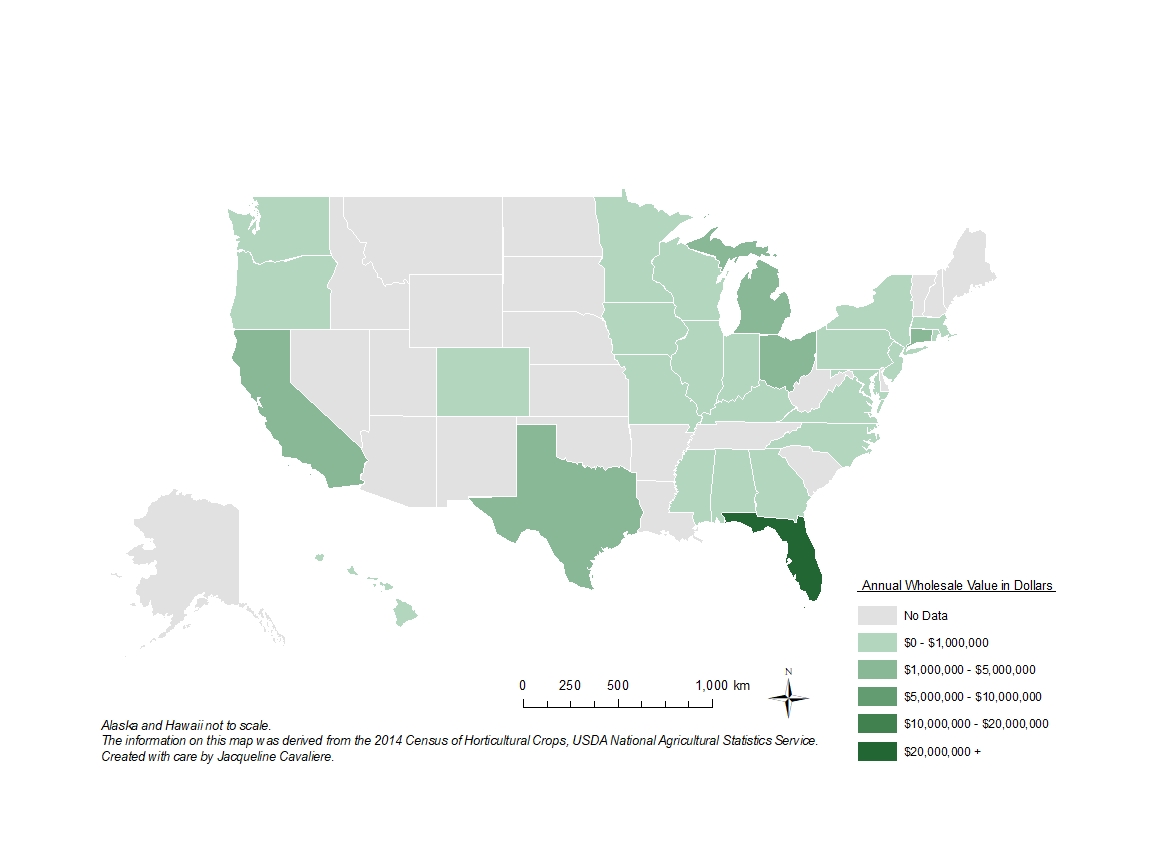
Main Diseases Problems
Leaf spots may be caused by several fungi. In most cases, cleaning up plant debris and removing infected leaves will provide adequate control. Southern stem blight may occur on hibiscus. To help prevent southern blight, keep mulch from touching the stems.
Main Pest Problems
Spider mites, aphids, scale, whiteflies, mealybugs and thrips.
IR-4 Research
Most of the research IR-4 has sponsored has been related to crop safety (112 trials and 62 products).
Authors
Allison Ballantyne, IR-4 Environmental Horticulture Program Assistant Manager
Jackie Cavaliere developed map of hibiscus sales
